3737. Is it a heap?
The Heap data structure can be implement using an array.
The array must maintain the
main Heap property: for each i (1 ≤ i ≤ n) next
conditions must hold:
·
If 2i ≤ n, then a[i] ≤ a[2i]
·
If 2i + 1 ≤ n, then a[i] ≤ a[2i + 1]
The array of integers is given. Determine whether it
is a Heap.
Input. First line contains number n (1 ≤ n
≤ 105). Second line contains n integers
that do not exceed 2 * 109 by absolute value.
Output. Print “YES”, if the array is
a Heap and “NO” otherwise.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
7 3 10 5 12 11 6 7 |
YES |
SOLUTION
heap
Algorithm analysis
For each index i of the input
array, the heap condition must be checked. It is enough to iterate over the
value of i from 1
to n / 2.
Example
The heap given
in the sample, has the
form:
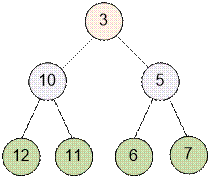
Algorithm realization
To store the input numbers, declare the array m.
#define MAX 100010
int m[MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
Move through
the array from the beginning to the middle. Check the heap condition. If at some iteration the condition
is not satisfyed, set flag = 1 and exit the loop.
flag =
0;
for (i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++)
{
if ((2 * i <= n) && (m[i] > m[2 * i]))
{
flag = 1; break;
}
if ((2 * i + 1 <= n) && (m[i] > m[2 * i + 1]))
{
flag = 1; break;
}
}
Depending on the value of the flag variable, print the answer.
if (flag == 1) printf("NO\n"); else printf("YES\n");
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=
n / 2; i++)
{
if ((2 * i <= n) && (m[i] > m[2 * i]))
{
flag = 1; break;
}
if ((2 * i + 1 <= n) && (m[i] > m[2 * i + 1]))
{
flag = 1; break;
}
}
if (flag == 1) System.out.println("NO");
else System.out.println("YES");
con.close();
}
}